Logistics benchmarking is a strategic process that involves comparing and evaluating the performance of logistics activities and processes within an organization against industry standards or the practices of leading companies. It allows companies to assess their logistical performance and identify areas for improvement by measuring their operations against predefined metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Ready to save on your freight costs? Experience the power of DFreight, your trusted digital freight forwarding partner. Get instant access to the best prices in the industry and streamline your logistics operations. Start optimizing your shipping expenses today, and click here to get a quote. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to maximize savings with DFreight!
Table of Contents
Definition of Logistics Benchmarking
Logistics benchmarking can be defined as the systematic measurement and comparison of an organization’s logistics performance metrics against established standards, industry best practices, or top-performing competitors. It involves analyzing various aspects of logistics operations, such as inventory management, transportation, warehousing, order fulfillment, and customer service, to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
Benchmarking can be conducted internally, where a company compares different departments or divisions within the organization, or externally, where the focus is on comparing performance with other companies in the same industry or sector. The objective is to identify areas of strength and weakness and implement strategies to enhance overall logistics efficiency and effectiveness.
Importance of Logistics Benchmarking
Logistics benchmarking plays a crucial role in driving continuous improvement and enhancing competitiveness in the dynamic business environment. Here are some reasons highlighting the importance of logistics benchmarking:
- Performance Evaluation: Benchmarking provides a means to objectively assess an organization’s logistics performance. By comparing key metrics and KPIs, companies can identify their position relative to industry standards and top performers. This evaluation helps to identify areas where improvements are required.
- Identification of Best Practices: Through benchmarking, companies can gain insights into best practices employed by leading organizations in the industry. By studying these practices, companies can adopt or adapt successful strategies to improve their own logistics processes.
- Goal Setting and Performance Targets: Logistics benchmarking enables companies to set realistic performance targets based on industry benchmarks and best practices. Organizations can align their efforts and resources by establishing clear targets to achieve desired results.
- Competitive Advantage: By benchmarking against industry leaders, companies can gain a competitive edge. It allows them to identify innovative approaches, technologies, or processes that can be implemented to outperform competitors and differentiate themselves in the market.
Benefits of Logistics Benchmarking
Logistics benchmarking offers several benefits to organizations striving for operational excellence and improved supply chain performance. Some key benefits include:
- Performance Improvement: Benchmarking identifies areas of improvement and provides a roadmap for enhancing logistics processes. By implementing changes based on benchmarking insights, companies can streamline operations, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Cost Reduction: Benchmarking helps identify cost drivers and inefficiencies within the logistics system. By comparing costs and practices with industry leaders, organizations can uncover opportunities for cost reduction, optimize resource allocation, and achieve better financial performance.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Benchmarking provides data-driven insights that support informed decision-making. It enables organizations to make strategic choices based on industry best practices and proven performance metrics, leading to more effective logistics strategies.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Organizations foster a culture of continuous improvement through benchmarking. They learn from industry peers, adapt to changing market conditions, and stay updated with emerging trends and technologies, positioning themselves for long-term success.
In summary, logistics benchmarking is a powerful tool that enables organizations to assess their logistics performance, identify improvement areas, and strive for excellence. By benchmarking against industry standards and best practices, companies can optimize their operations, achieve cost savings, and gain a competitive advantage in the ever-evolving logistics landscape
Key Metrics and Indicators for Logistics Benchmarking
When conducting logistics benchmarking, it is essential to focus on key metrics and indicators that provide valuable insights into the performance of various logistics functions. Here are some important metrics to consider for different aspects of logistics operations:
Inventory Management Metrics
Effective inventory management is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and ensuring timely order fulfillment. The following metrics are commonly used to evaluate inventory management performance:
- Inventory Turnover: Measures how quickly inventory is sold or used over a specific period. It indicates the efficiency of inventory utilization and can highlight potential issues such as excess stock or stockouts.
- Stock Accuracy: Reflects the accuracy of inventory records compared to the actual physical inventory. High stock accuracy ensures reliable order fulfillment and minimizes discrepancies.
- Fill Rate: Measures the percentage of customer orders that can be fulfilled from available inventory without backorders or delays. A high fill rate indicates a well-managed inventory system.
Transportation Metrics
Efficient transportation management is vital for timely and cost-effective delivery of goods. The following metrics help evaluate transportation performance:
- On-time Delivery: Measures the percentage of shipments delivered within the agreed-upon timeframe. It reflects the reliability and efficiency of transportation operations.
- Transit Time: Calculates the average time taken for goods to reach their destination from the time of shipment. Monitoring transit time helps identify potential bottlenecks and optimize transportation routes.
- Freight Cost per Unit: Determines the average cost of transportation per unit of goods shipped. Tracking this metric helps identify cost-saving opportunities and evaluate the efficiency of transportation spend.
Warehousing Metrics
Efficient warehousing operations are critical for timely order processing, inventory management, and minimizing storage costs. The following metrics are commonly used to assess warehousing performance:
- Order Cycle Time: Measures the time taken to process an order from receipt to shipment. A shorter order cycle time indicates efficient warehousing operations and faster order fulfillment.
- Storage Utilization: Calculates the percentage of available storage space being utilized. Optimizing storage utilization helps minimize storage costs and maximize warehouse efficiency.
- Order Accuracy: Reflects the percentage of orders fulfilled without errors. High order accuracy is crucial for customer satisfaction and minimizing returns or rework.
Order Fulfillment Metrics
Order fulfillment metrics focus on the efficiency and accuracy of the entire order fulfillment process. Key metrics in this category include:
- Order Lead Time: Measures the time taken from order placement to delivery. Shorter lead times enhance customer satisfaction and competitiveness.
- Perfect Order Rate: Reflects the percentage of orders fulfilled without any errors or issues. A high perfect order rate indicates an effective order fulfillment process.
- Backorder Rate: Calculates the percentage of orders that cannot be fulfilled immediately due to stock unavailability. A lower backorder rate indicates better inventory management and customer service.
Customer Service Metrics
Customer service metrics help evaluate the quality of service provided to customers. Important metrics in this category include:
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Assesses customers’ overall satisfaction with the logistics service. Regular CSAT surveys help identify areas for improvement and measure customer loyalty.
- On-time Delivery Performance: Measures the percentage of orders delivered on time as promised to customers. Consistently meeting delivery deadlines enhances customer satisfaction and builds trust.
- Response Time: Measures the time taken to respond to customer inquiries or issues. Faster response times contribute to improved customer experience and loyalty.
By analyzing and comparing these key metrics and indicators, companies can identify areas of strength and weakness, set performance targets, and implement strategies to enhance their logistics operations and achieve better results.
Steps to Conduct Logistics Benchmarking
It is important to follow a systematic approach to conduct logistics benchmarking and drive improvement in your logistics operations. The following steps outline the process of conducting logistics benchmarking:
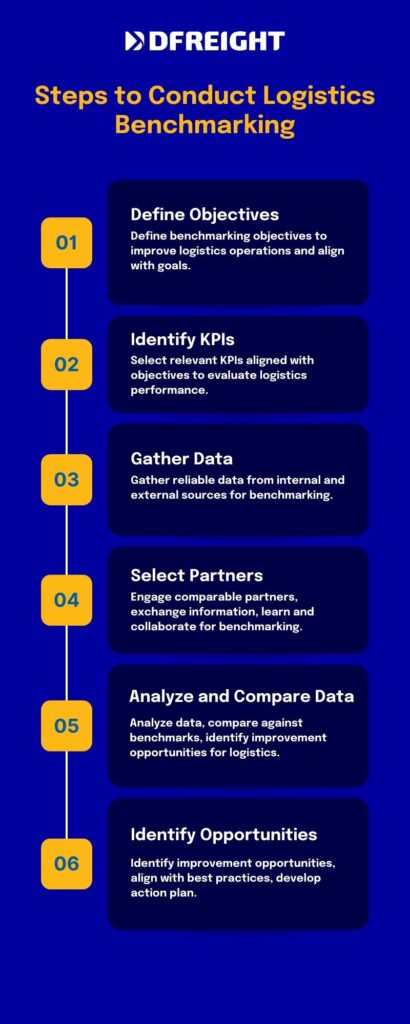
Define Benchmarking Objectives
Start by clearly defining the objectives of your benchmarking initiative. Determine the specific areas of your logistics operations that you want to benchmark and improve. For example, you may focus on transportation costs, warehouse efficiency, or order fulfillment accuracy. Setting clear objectives will guide the benchmarking process and ensure alignment with your organization’s goals.
Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure and evaluate the performance of your logistics operations. These KPIs should align with your benchmarking objectives and provide meaningful insights into your performance. Refer to industry best practices, internal data, and relevant industry standards to identify the most relevant KPIs for your benchmarking exercise.
Gather Data and Establish Baselines
Collect accurate and reliable data related to your selected KPIs. This data can come from internal sources such as your enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, transportation management system (TMS), or warehouse management system (WMS). Additionally, gather external data from industry associations, research reports, or benchmarking databases to establish industry benchmarks and reference points. Use this data to establish baseline performance levels for your logistics operations.
Select Benchmarking Partners
Identify benchmarking partners that are comparable to your organization in terms of industry, size, and logistics operations. These partners can be organizations that are recognized as industry leaders or those with exemplary performance in specific logistics functions. Engage in discussions and collaboration with these partners to exchange information, compare practices, and learn from their experiences. Establishing trust and confidentiality agreements with your benchmarking partners is important to ensure the integrity and security of shared data.
Analyze and Compare Performance Data
Analyze and compare your performance data against the established baselines and the data provided by your benchmarking partners. Look for gaps, variations, and areas where you are underperforming compared to the benchmarks or your partners. Identify trends and patterns in the data to gain insights into potential improvement areas. Use data visualization techniques such as charts, graphs, or dashboards to facilitate the analysis process and make it easier to identify opportunities for improvement.
Identify Improvement Opportunities
Based on the analysis of the benchmarking data, identify specific improvement opportunities for your logistics operations. Consider best practices and successful strategies employed by your benchmarking partners. Evaluate potential changes, process enhancements, or technology implementations that can help you bridge the performance gaps and achieve your benchmarking objectives. Develop an action plan that outlines the steps, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing these improvement initiatives.
By following these steps, organizations can conduct effective logistics benchmarking exercises and gain valuable insights into their performance. This process enables informed decision-making, drives continuous improvement, and positions companies for enhanced logistics performance and competitiveness.
Overcoming Challenges in Logistics Benchmarking
While logistics benchmarking offers numerous benefits, organizations may encounter certain challenges throughout the process. It is important to be aware of these challenges and develop strategies to overcome them. Here are some common challenges in logistics benchmarking and ways to address them:
Data Collection and Analysis Challenges
Collecting accurate and reliable data can be a significant challenge in logistics benchmarking. Organizations may face issues such as incomplete or inconsistent data, data silos, or a lack of standardized measurement systems. To overcome these challenges:
- Standardize Data: Develop clear data collection protocols and establish standardized measurement systems across the organization. This ensures consistency and comparability of data.
- Invest in Data Management Systems: Implement robust data management systems, such as an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system or a transportation management system (TMS), to streamline data collection, storage, and analysis processes.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Regularly validate and verify data to ensure accuracy. Conduct audits and checks to identify and resolve any data discrepancies or errors.
Identifying Suitable Benchmarking Partners
Finding suitable benchmarking partners can be a challenge, especially when organizations operate in unique industries or have specific logistics requirements. To overcome this challenge:
- Industry Associations and Networks: Engage with industry associations, trade groups, or logistics networks to identify potential benchmarking partners. These organizations often provide platforms for collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Research and Referrals: Conduct thorough research to identify companies in your industry that have a reputation for excellence in logistics. Seek referrals from industry experts or trusted contacts.
- Customized Approach: If it is challenging to find direct benchmarking partners, consider adopting a customized approach by benchmarking different aspects of your logistics operations with different organizations that excel in those specific areas.
Addressing Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common challenge when implementing improvement initiatives identified through benchmarking. To address resistance to change:
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly communicate the benefits of benchmarking and the potential improvements it can bring to the organization. Highlight how benchmarking can lead to increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Involve Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders and employees from different levels of the organization in the benchmarking process. This creates a sense of ownership and involvement, increasing their willingness to embrace change.
- Provide Training and Support: Offer training programs and support to employees to enhance their skills and knowledge related to the proposed changes. Address any concerns or questions they may have and provide ongoing support throughout the implementation process.
Ensuring Confidentiality and Data Security
Sharing sensitive data and information with benchmarking partners may raise concerns about confidentiality and data security. To ensure confidentiality and data security:
- Establish Confidentiality Agreements: Implement formal agreements with benchmarking partners that clearly outline the terms and conditions regarding data sharing, confidentiality, and intellectual property protection.
- Anonymize Data: When sharing data with benchmarking partners, anonymize the data to remove any identifying information. This protects the confidentiality of the data while still allowing for meaningful benchmarking comparisons.
- Secure Data Infrastructure: Implement robust data security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and firewalls, to protect data within the organization. Regularly update and audit these security measures to stay ahead of potential threats.
By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can navigate the logistics benchmarking process effectively and derive maximum value from the insights gained. Overcoming these challenges paves the way for informed decision-making, continuous improvement, and enhanced logistics performance.
Closing Remarks
It is important to remember that logistics benchmarking is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing process. Regularly reassessing performance, adapting to changing market dynamics, and embracing a culture of continuous improvement are key to unlocking the full potential of logistics benchmarking.
By embracing logistics benchmarking and leveraging the insights it provides, organizations can optimize their logistics operations, deliver value to customers, and position themselves as leaders in the ever-evolving logistics industry.
What is logistics benchmarking?
Logistics benchmarking is the process of comparing and evaluating the performance of various logistics functions and processes within an organization against industry standards, best practices, or other companies. It involves measuring key metrics and indicators to identify areas for improvement and drive performance enhancement in logistics operations.
Why is logistics benchmarking important?
Logistics benchmarking is important because it provides organizations with valuable insights into their performance and allows them to identify opportunities for improvement. By comparing their operations with industry benchmarks or best-in-class companies, organizations can identify gaps, set performance targets, and implement strategies to enhance their logistics efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
How do I select suitable benchmarking partners?
Selecting suitable benchmarking partners involves identifying companies or organizations that are comparable to your own in terms of industry, size, and logistics operations. Look for organizations that excel in specific logistics functions or are recognized as industry leaders. Engaging with industry associations, trade groups, or logistics networks can also help identify potential benchmarking partners.
What are some common challenges in logistics benchmarking?
Common challenges in logistics benchmarking include data collection and analysis challenges, identifying suitable benchmarking partners, addressing resistance to change, and ensuring confidentiality and data security. Overcoming these challenges requires implementing standardized data collection processes, engaging in thorough research, involving stakeholders, and establishing confidentiality agreements and data security measures.
How often should I conduct logistics benchmarking?
The frequency of conducting logistics benchmarking depends on various factors such as the industry dynamics, the rate of organizational change, and the availability of data. It is recommended to conduct benchmarking exercises periodically, such as annually or biennially, to track progress, identify new improvement areas, and stay updated with evolving industry practices.














